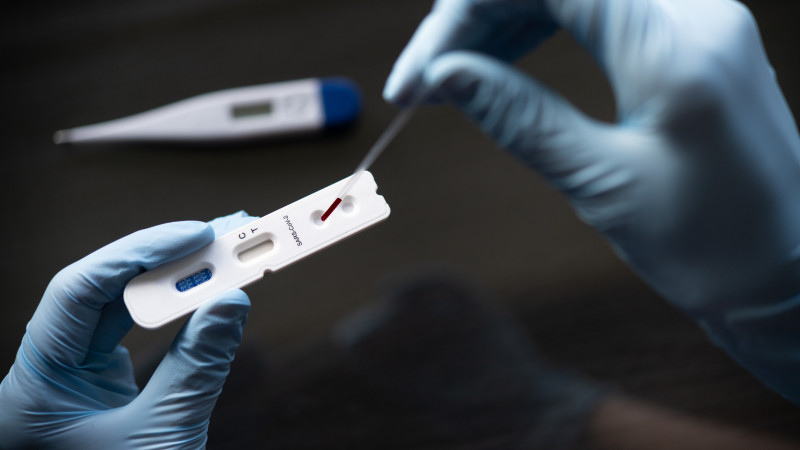
In recent months, the specialists have created several versions of test systems that determine traces of the SARS-CoV-2 virus presence in patients’ blood samples or secretions. They are based either on detection of RNAi fragments of the causative agent of the COVID-19 disease using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and its analogs, or presence of coronavirus antibodies.
Such a test usually takes a lot of time, from 30 minutes to several hours, which forces scientists to look for new, faster ways to diagnose coronavirus infection. For example, Russian and Lithuanian biologists recently accelerated testing 13 times by creating a new method of group testing using PCR.
The scientists of Florida State University are developing fundamentally different test systems that detect traces of SARS-CoV-2 in other ways. In particular, molecular biologists have adapted the CRISPR/Cas12 genomic editor for these purposes, making on its basis a test that does not make false positives when studying biofluid samples.
Source: https://nauka.tass.ru/nauka/11405447
Photos are from open sources.